example of purposive sampling in quantitative research|purposive sampling in research example : mfg Presenting individual case studies has highlighted how purposive sampling can be integrated into varying contexts dependent on study design. The sampling strategies clearly situate each study in terms of trustworthiness for . Plataforma destinada aos Mlk Sonhador que estão no corre da vida! Plataforma destinada aos Mlk Sonhador que estão no corre da vida! Este site usa cookies para garantir que você obtenha a melhor experiência de navegação Saber mais. Aceitar! Bem-vindo ao Xerecrazy
{plog:ftitle_list}
bibivitona. cosplay_ gabrieladutra. moda_ godsinjury. ilustração_ l0spe. lifestyle_ 99lua. vtuber_ vivi. dança_ arielsaorii. streaming_ viqsm. Vamos juntos para o seu próximo nível? conheça. 2024 ® s2vips.com
what is purposive sampling in qualitative research
moisture meter aubuchon hardware
Example: Step-by-step purposive sampling. Purposive sampling is widely used in qualitative research, when you want to focus in depth on a certain phenomenon. There are . Presenting individual case studies has highlighted how purposive sampling can be integrated into varying contexts dependent on study design. The sampling strategies clearly situate each study in terms of trustworthiness for .Purposive sampling is a non-probability method for obtaining a sample where researchers use their expertise to choose specific participants that will help the study meet its goals. These subjects have particular characteristics that the . In purposive sampling, the final sample is typically a subset of the population with similar features. The idea behind purposive sampling is to select cases, individuals, or communities that serve as the dataset from which .
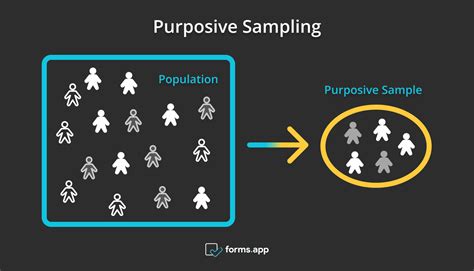
Purposive sampling (also known as judgment, selective or subjective sampling) is a sampling technique in which researcher relies on his or her own judgment when choosing members of population to participate in the study.
Purposive sampling is often used in qualitative research, as it allows the researcher to focus on specific areas of interest and gather in-depth data on those topics. It is . Indeed, purposive stratified sampling allows for the exploration of a range of variations and differences (Patten, 2002), with the purpose of stratification being to capture .A purposive sample, also referred to as a judgmental or expert sample, is a type of nonprobability sample. The main objective of a purposive sample is to produce a sample . Also known as subjective sampling, purposive sampling is a non-probability sampling technique where the researcher relies on their discretion to choose variables for the .
This research uses interview and focus group discussion (FGD) study methods to obtain various information. Purposive sampling was used to determine the research area (Nyimbili and Nyimbili, 2024 .
Here’s a simple example of how purposive sampling works in market research: . Adopting purposive sampling for your research helps you to extract lots of information from research participants, especially when there are just a few of them. On the flip side, it can ruin your data collection process if you make subjective or generalized . A purposive sample is one that is selected based on characteristics of a population and the purpose of the study. Learn more about it. . Expert sampling is a form of purposive sampling used when research .sampling, a researcher first identifies relevant categories of people (e.g., male, female; under age of 30, over the age of 30), then decides how many to get in each category. Thus, the number of people in various categories of the sample is fixed. c. Purposive or Judgmental Sample i. Purposive sampling is an acceptable kind of sampling
what does purposive sampling mean
The sampling technique in quantitative research comes from its ability to draw small units of the population (i.e., sample size) and generalize it to the population (Seddon & Scheepers, 2012).In a study, specifically in behavioural research where the number of population elements is too large, collecting data from every element of a population is unreal. When to use purposive sampling. Purposive sampling is best used when you want to focus in depth on relatively small samples.Perhaps you would like to access a particular subset of the population that shares certain characteristics, or you are researching issues likely to have unique cases.. The main goal of purposive sampling is to identify the cases, .3.4 Sampling Techniques in Quantitative Research Target Population. The target population includes the people the researcher is interested in conducting the research and generalizing the findings on. 40 For example, if certain researchers are interested in vaccine-preventable diseases in children five years and younger in Australia. The target population will be all children aged . Expert purposive sampling is used when the researcher needs to obtain knowledge from individuals with particular expertise. This skill may be necessary during the starting phase of qualitative research design because it can help understand new areas of interest. Purposive Sampling Example. Purposive sampling can be used in educational .
Purposive Sampling Examples and Use Cases. We know the definition of purposive sampling and different ways of carrying out purposive sampling. Now, let’s check out some examples of where it’s used. Use Case #1: Choosing a Candidate. The first and most obvious example of purposive sampling is choosing skilled candidates for a vacancy.
What is Purposive Sampling? Methods, Techniques, and Examples Purposive (judgmental) sampling. Purposive sampling is a blanket term for several sampling techniques that choose participants deliberately due to qualities they possess. It is also called judgmental sampling, because it relies on the judgment of the researcher to select the units (e.g., people, cases, or organizations studied).
This chapter explains how to design suitable sampling strategies for qualitative research. The focus of this chapter is purposive (or theoretical) sampling to produce credible and trustworthy explanations of a phenomenon (a specific aspect of society). A specific research question (RQ) guides the methodology (the study design or approach).It defines the .Stratified random sampling. Stratified random sampling is similar to simple random sampling, but it kicks things up a notch. As the name suggests, stratified sampling involves selecting participants randomly, but from within certain pre-defined subgroups (i.e., strata) that share a common trait.For example, you might divide the population into strata based on gender, . The research employed a pre-experimental research design, with a one-group pre-test and post-test approach, utilizing a sample of 30 IX C students selected through cluster random sampling methodology.Purposive sampling. Purposive sampling, also known as judgmental, selective or subjective sampling, is a type of non-probability sampling technique.Non-probability sampling focuses on sampling techniques where the units that are investigated are based on the judgement of the researcher [see our articles: Non-probability sampling to learn more about non-probability .
Knowledge of sampling methods is essential to design quality research. Critical questions are provided to help researchers choose a sampling method. This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration.Background: Purposive sampling has a long developmental history and there are as many views that it is simple and straightforward as there are about its complexity. The reason for purposive sampling is the better matching of the sample to the aims and objectives of the research, thus improving the rigour of the study and trustworthiness of the data and results.
Purposive sampling may also be used with both qualitative and quantitative research techniques. . tested against random probability sampling. Choosing the purposive sample is fundamental to the .KEY WORDS: purposive sampling, qualitative, sample Sampling and purposive sampling . The nature of the research (e.g. quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods).SAMPLING. Sampling can be defined as the process through which individuals or sampling units are selected from the sample frame. The sampling strategy needs to be specified in advance, given that the sampling method may affect the sample size estimation. 1,5 Without a rigorous sampling plan the estimates derived from the study may be biased (selection bias). 3As utilized in qualitative and mixed methods research, purposive sampling involves an iterative process of selecting research subjects rather than starting with a predetermined sampling frame.Akin to grounded theory, the selection process involves identifying themes, concepts, and indicators through observation and reflection (Schutt, 2006: 348).). Schutt places particular .
Convenience sampling. Purposive sampling. Voluntary response sampling. Snowball sampling. Quota sampling. Convenience sampling. The strategy of convenience sampling is to choose your sample quickly and efficiently, using the least effort, usually to save money. Let's say you want to survey the opinions of 100 millennials about a particular topic. When using purposive sampling, the researcher has the freedom to choose a sample size he/she/they think have the best suitable characteristics to give him/her/them an in-depth and quality .1. Purposive Sampling. Purposive sampling, or judgmental sampling, is a non-probability sampling technique in qualitative research that’s commonly used. In purposive sampling, researchers intentionally select participants with specific characteristics or unique experiences related to the research question. The chapter discusses different types of sampling methods used in qualitative research to select information-rich cases. Two types of sampling techniques are discussed in the past qualitative .
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive, allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.. Qualitative research example If you want to generate new ideas for online teaching strategies, a qualitative approach would make the most sense. You can use this type of research to explore exactly . Non-probability sampling is at higher risk than probability sampling for research biases like sampling bias. Example: Non-probability sampling You are investigating the coping mechanisms of employees dealing with workplace stress. You want to conduct expert interviews with organizational psychologists to get their viewpoint on the topic.

web29 de out. de 2023 · Por Redação Marie Claire. 29/10/2023 08h32 Atualizado há 3 meses. Entenda a briga de Amabylle Eiroa e Graciele Lacerda — Foto: Reprodução Instagram. .
example of purposive sampling in quantitative research|purposive sampling in research example